Cholesterol efflux capacity
Members
Principal Investigator (PI)
Co-PI
Team
Stefan Coassin , Sebastian Schönherr , Claudia Lamina , Gertraud Streiter , Lukas Forer , Azin Kheirkhah
About
HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC) is defined as the ability of HDL particles to induce efflux of cholesterol from peripheral cells such as macrophages. Epidemiological studies have shown that it is inversely associated with cardiovascular disease in the general population and it may protect from atherosclerosis. We are interested in identifying genetic and non-genetic determinants of CEC and understanding if CEC is also associated with disease in other cohorts. Since tackling these questions requires CEC measurements in large study cohorts, we are also interested in the technical aspects of measuring CEC.
High-throughput measurement of HDL-mediated CEC
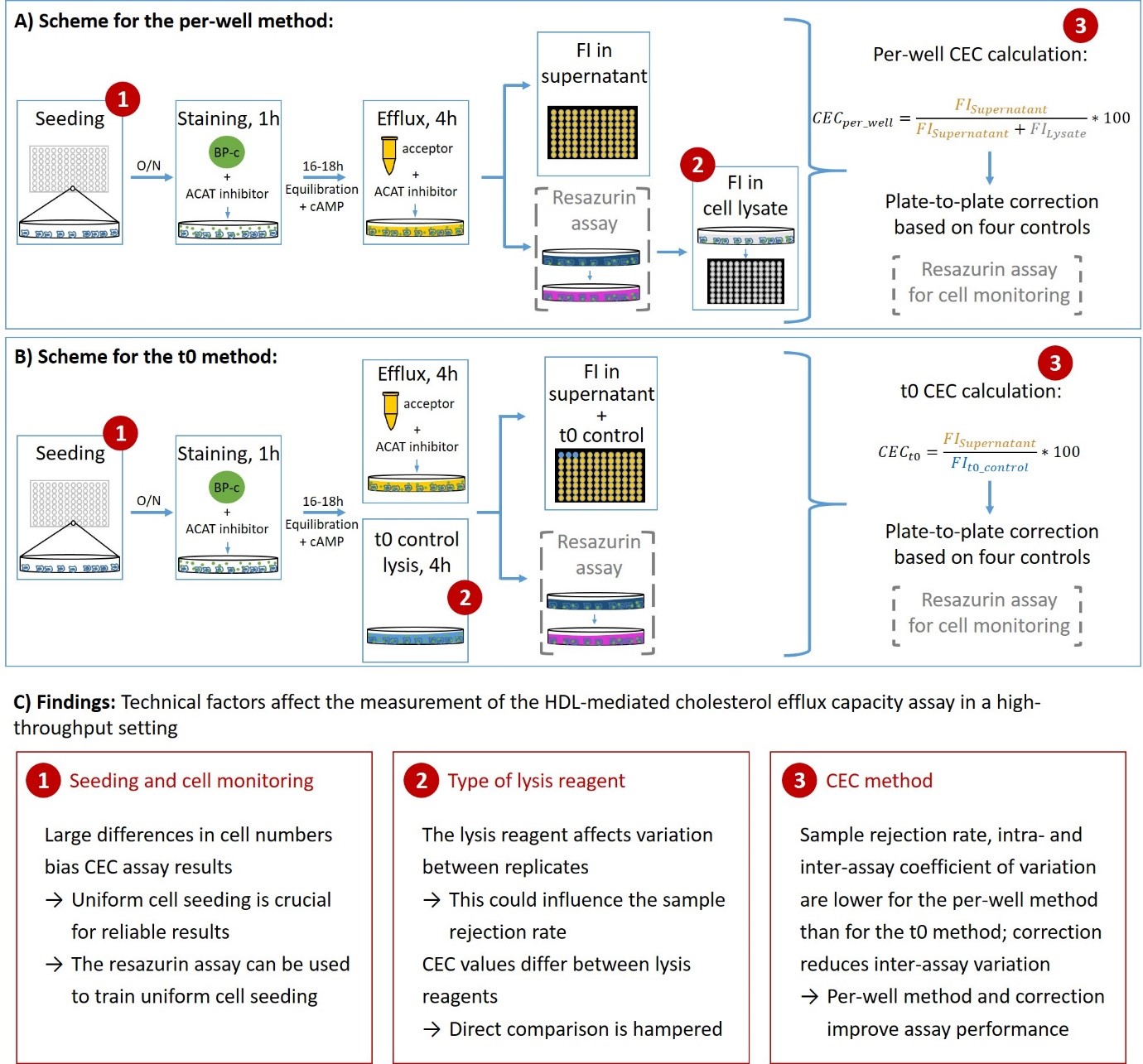
HDL-mediated CEC can be measured in vitro using a cell-based assay. However, the availabe assays are not well standardized and different protocols have been published. In an effort to have a high-throughput protocol to measure CEC in a reproducible manner we 1) searched published CEC protocols for technical differences, 2) systematically tested technical factors that can influence CEC measurement and 3) tested a high-throughput CEC protocol and quality control measures to determine a reliable high-throughput CEC protocol. We identified that type of lysis reagent, cell numbers and the calculation method of CEC as technical factors influence quality of CEC measurements (Figure 1) and provide a detailed protocol with extensive quality control to measure CEC (Schachtl-Riess JF et al. J Lipid Res 2021).
Cooperations
GCKD study, CAVASIC study, Department of Internal Medicine II (Medical University of Innsbruck)
Publications
Schachtl-Riess JF, Coassin S, Lamina C, Demetz E, Streiter G, Hilbe R, Kronenberg F: Lysis reagents, cell numbers, and calculation method influence high-throughput measurement of HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity. J. Lipid Res. 62:100125, 2021. PMID: 34571016 Journal Article
Kronenberg F: HDL in CKD-the devil is in the detail. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 29:1356-1371, 2018. PMID: 29472417 Review
Schachtl-Riess JF, Schönherr S, Lamina C, Forer L, Coassin S, Streiter G, Kheirkhah A, Li Y, Meiselbach H, Di Maio S, Eckardt KU, Köttgen A, Kronenberg F, GCKD investigators: KLKB1 and CLSTN2 are associated with HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity in a genome-wide association study. Atherosclerosis 368:1-11, 2023. PMID: 36812656 Journal Article