Lipoprotein(a) Genomics
We are interested in understanding how genetic variants in LPA contribute to the huge variance in lipoprotein(a) concentrations observed between individuals and across ancestries.
Lead
Co-Lead

Professor of Computational Genomics
+43 512 9003 70579
sebastian.schoenherr@i-med.ac.at
Team

Lab technician (BMA) (on maternal leave)
+43 512 9003 70573
gertraud.streiter@i-med.ac.at

Bachelor Student Molecular Medicine
About
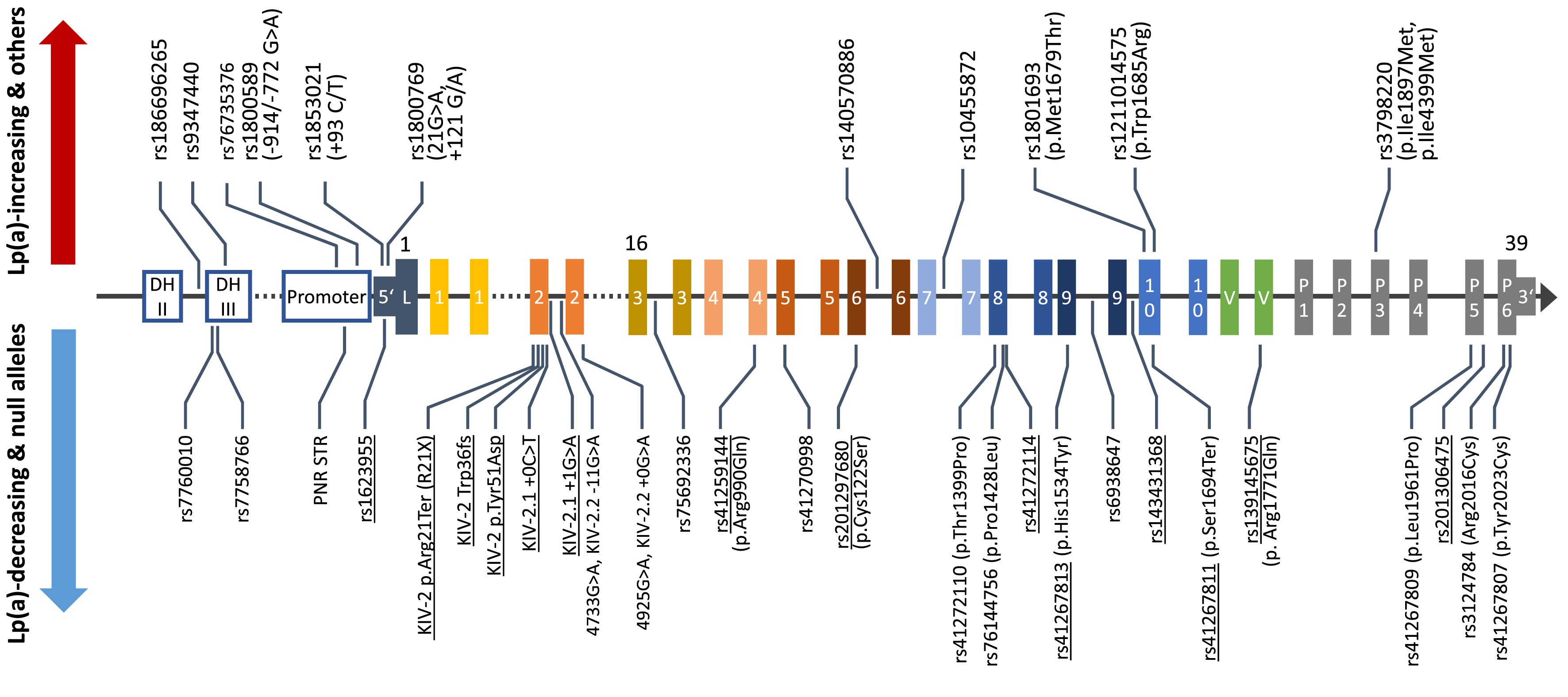
Genetic variation in the LPA gene explains up to 90% of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] plasma concentrations in the population but the genetic mechanisms that govern the individual lipoprotein(a) concentrations are poorly understood. We investigate how functional genetic variants in LPA create the huge variance in lipoprotein(a) concentrations that we observe between individuals and across ancestries. A major part of our work concerns the investigation of mutations located in the KIV-2 repeat region of the LPA gene. This repetitive region can encompass up to 70% of the coding sequence of the gene, but, due to its complex structure, it has not been accessible until recently. By combining the computational expertise of the institute in the detection of low-level mutations, advanced molecular techniques genetics and our long-standing experience in Lp(a) research, we have developed a comprehensive genetic toolset capable of adressing many difficult aspects of Lp(a) genetics. Additionally, we enjoy exploring the potential of nanopore sequencing and other emerging genetic technologies to tackle tough genetic questions across disciplines.
Nanopore Sequencing
Nanopore sequencing allows sequencing DNA and RNA molecules by monitoring fluctuations in the ionic current while a DNA or RNA strand moves through a protein pore. Unlike other technologies, Nanopore sequencing provides data in real-time, allows up to megabase-sized read lengths, reads directly the native target molecule, provides true single molecule data and keeps information about epigenetic modifications. It also allows direct phasing of variants over long DNA segments, which is of special use in Lp(a) genetics. These features make it an appealing technology to target complex genes with structural variants and extensive homologies like the LPA gene. We explore applications of this technologies in Lp(a) genetics and beyond (such as human genetics, variant phasing, DNA/RNA epigenetics and metagenomics).

Join the team
MolMed Lab side teaching, project studies and theses (MolMed Bachelor, MolMed Master, Medicine) available! If you are interested, contact stefan.coassin@i-med.ac.at. Available topics may involve genetic analysis of complex gene regions, applications of Nanopore sequencing and related bioinformatics, or functional characterization of SNPs.
Technologies in our Lab
- Nanopore sequencing (ONT MinION and PromethION P2 systems)
- Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR)
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS)
- A comprehensive toolbox of advanced PCR tsorechnologies
- High-throughput genotyping of KIV-2 variants by ddPCR, allele-specific qPCR or castPCR
- Roboter-assisted high-throughput qPCR and TaqMan genotyping
- Sanger Sequencing
- Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) (LPA allele sizing and mutation phasing, HMW DNA assessment)
- HepG2 cell lines expressing various apolipoprotein(a) isoforms
- Cloning techniques, minigene splicing assays and luciferase reporter assays
Other GenEpi Investigators involved
- The Computational Lab: Hansi Weissensteiner , Lukas Forer
Funding and Projects
- Austrian Science Fund (FWF) PAT-5152823: Multi-ancestry LPA KIV-2 haplotype analysis and imputation (2024-)
- Intramural funding (2022-)
- Austrian Science Fund (FWF) P31458-B34: Investigation of the molecular effects of the LPA KIV-2 mutation 4925 G>A (2018-2023)
- Austrian Atherosclerosis Society: New avenues for understanding Lp(a) concentrations in families (2018-2020)
- D•A•CH-Society for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases Startup grant (2015‐2017)
- Intramural funding MUI-START (2015-2017)
Earlier Team Members and Students
- Bachelor theses: Johanna Schachtl-Riess (2015), Paul Bichler (2015), Gertraud Erhart (2016), Jamie Lee Losso (2016)
- Master theses: Silvia Di Maio (2018), Peter Zöscher (2021), Stephan Amstler (2023)
- PhD theses: Rebecca Grüneis (2023), Silvia Di Maio (2024)
- Post-Doc and Staff: Monika Summerer, Jamie Lee Losso
Key Publications
Coassin S, Kronenberg F: Lipoprotein(a) beyond the kringle IV repeat polymorphism: The complexity of genetic variation in the LPA gene. Atherosclerosis 349:17-35, 2022. PMID: 35606073 Review
Amstler S, Streiter G, Pfurtscheller C, Forer L, Di Maio S, Weissensteiner H, Paulweber B, Schönherr S, Kronenberg F, Coassin S: Nanopore sequencing with unique molecular identifiers enables accurate mutation analysis and haplotyping in the complex lipoprotein(a) KIV-2 VNTR. Genome Med. 16:117, 2024. PMID: 39380090 Journal Article
Grüneis R, Weissensteiner H, Lamina C, Schönherr S, Forer L, Di Maio S, Streiter G, Peters A, Gieger C, Kronenberg F, Coassin S: The kringle IV type 2 domain variant 4925G>A causes the elusive association signal of the LPA pentanucleotide repeat. J. Lipid Res. 63:100306, 2022. PMID: 36309064 Journal Article
Grüneis R, Lamina C, Di Maio S, Schönherr S, Zoescher P, Forer L, Streiter G, Peters A, Gieger C, Köttgen A, Kronenberg F, Coassin S: The effect of LPA Thr3888Pro on lipoprotein(a) and coronary artery disease is modified by the LPA KIV-2 variant 4925G>A. Atherosclerosis 349:151-159, 2022. PMID: 35534298 Journal Article
Schachtl-Riess JF, Kheirkhah A, Grüneis R, Di Maio S, Schoenherr S, Streiter G, Losso JL, Paulweber B, Eckardt KU, Köttgen A, Lamina C, Kronenberg F, Coassin S, GCKD Investigators: Frequent LPA KIV-2 variants lower lipoprotein(a) concentrations and protect against coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 78:437-449, 2021. PMID: 34325833 Journal Article
Di Maio S, Grüneis R, Streiter G, Lamina C, Maglione M, Schoenherr S, Öfner D, Thorand B, Peters A, Eckardt KU, Köttgen A, Kronenberg F, Coassin S: Investigation of a nonsense mutation located in the complex KIV-2 copy number variation region of apolipoprotein(a) in 10,910 individuals. Genome Med. 12:74, 2020. PMID: 32825847 Journal Article
Coassin S, Schönherr S, Weissensteiner H, Erhart G, Forer L, Losso JL, Lamina C, Haun M, Utermann G, Paulweber B, Specht G, Kronenberg F: A comprehensive map of single-base polymorphisms in the hypervariable LPA kringle IV type 2 copy number variation region. J. Lipid Res. 60:186-199, 2019. PMID: 30413653 Journal Article
Coassin S, Erhart G, Weissensteiner H, Eca Guimarães de Araújo M, Lamina C, Schönherr S, Forer L, Haun M, Losso JL, Köttgen A, Schmidt K, Utermann G, Peters A, Gieger C, Strauch K, Finkenstedt A, Bale R, Zoller H, Paulweber B, Eckardt KU, Hüttenhofer A, Huber LA, Kronenberg F: A novel but frequent variant in LPA KIV-2 is associated with a pronounced Lp(a) and cardiovascular risk reduction. Eur. Heart J. 38:1823-1831, 2017. PMID: 28444229 Journal Article





